Understanding Autism
In 2017 it was estimated that one in every 68 children born in the USA was subsequently diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The rate continues to increase and many other "developed" countries have rates that are similar to the USA, viz: Hong Kong (1 in 27), South Korea (1 in 38), Japan (1 in 55), Ireland (1 in 65). In Australia the rate has been steadily increasing and in 2009, 2012, 2015, the rate in the 5-9 age group has increased from 1.4 to 2.5, to 2.8% of the population. As these group age, the incidence increases in the 10-14, 15-19, 20-24 and over 45 yo groups. If one is to study the statistics more closely one can clearly see that some event or change has occurred in the population, that was initiated around 25 years ago, which has resulted in the ever increasing rise in the condition. Thus in 2009, the incidence in the 25+ group was only 0.1%, and in 2012, was 0.2%, and 2015, 0.3%. Extrapolating these figures back to year of birth, this would represent 0.1% in 1984, 0.2% in 1987 and 0.3% in 1990. Interestingly the original Slip, Slop, Slap campaign for sun protection occurred in 1981.A recent study in the Boston area (USA) looked at Developmental Disabilities (DD) in a cohort of 996 children. The rate of DD was extremely high, with only 32.8% who were neurotypical, whilst 30.5% had ADHD + ASD, 25.8% had ADHD only, and 6.6% had ASD only (Ji etal, 2020). The rate of increase has been astoundingly fast, and autism was only added to the NDIS in Australia in 2013.
https://www.aijw.gov.au/reports/disability/autism-in-australia/contents/autism
The cost of autism to society is ever increasing and is generally born by the community with over 75% of the income to support these individuals coming from a disability support pension, with fewer than 5% of individuals gaining paid employment.
The majority of people with autism, currently are under the age of 25, but with time, if the developmental delay is not resolved there will be a shift to the older population. (Projected rates for Australia are graphed below).
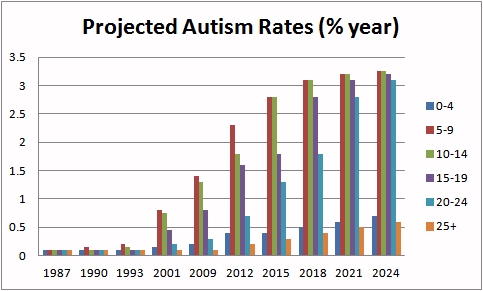
In an alarming trend, autism rates in Australia and Japan are now the highest in the world.
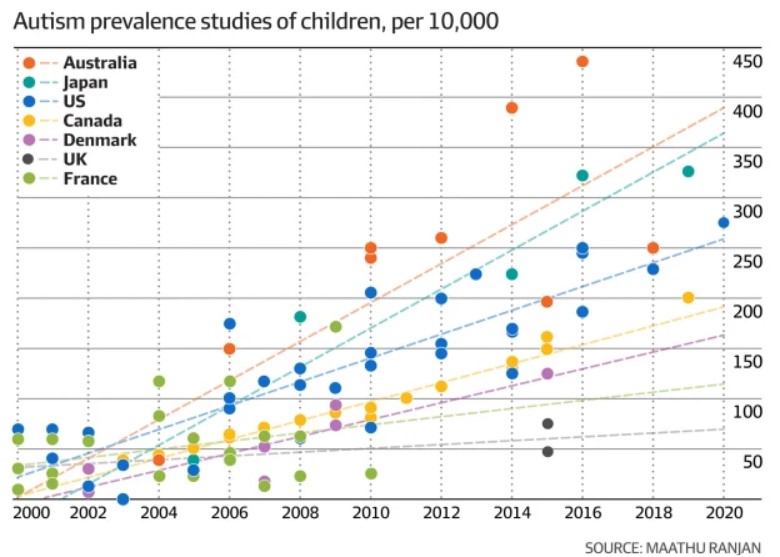
It has been postulated that " It is plausible that the growth of prevalence rates above the global average in Australia can be attributed to the financial incentives created by government policy, specifically the implementation of the NDIS". More than 8% of 5-8 year old children are on the NDIS in Australia.
Over the years many, many different theories have been put forward to explain the development of the condition, ranging from childhood vaccination, exposure to farming chemicals, exposure to organophosphates, exposure to methyl mercury, exposure to pyrethroids, etc. This has also given rise to a whole range of ineffective treatment regimes. Despite all of these theories, it is our belief that the development of ASD can be logically explained biochemically and we have pooled our data from over 1000 children with autism of various ages to develop a relatively simple theory on why the condition has developed and thereby devise a uniform strategy to try to correct the delayed development seen in these individuals.
The rapid increase in the rate of autism, and the observation that the development delay can largely be reversed strongly suggests that the condition cannot be explained by genetic variation (Folstein 2001; Mazumdar etal, 2010), and so we have excluded the discussion of this, however we have examined the genetics in over 200 children and have confirmed this (data not shown).
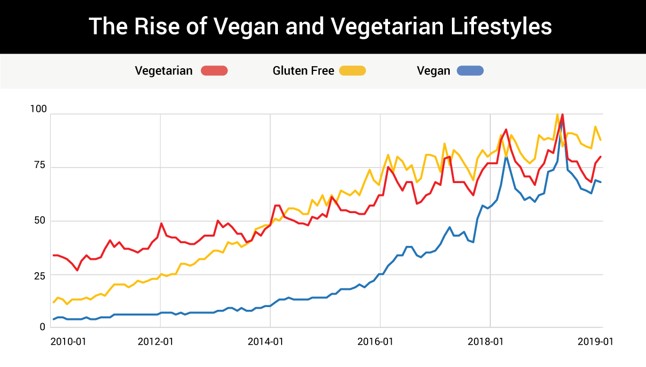
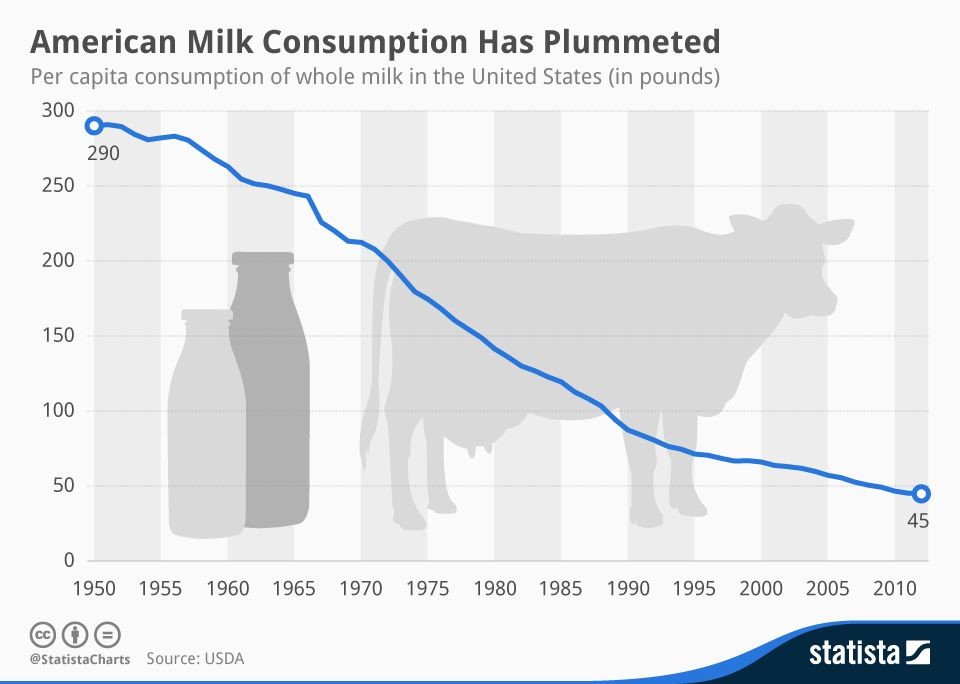
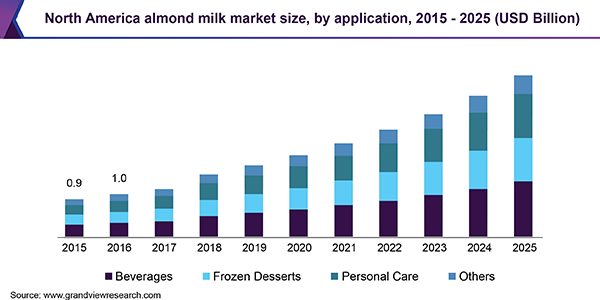
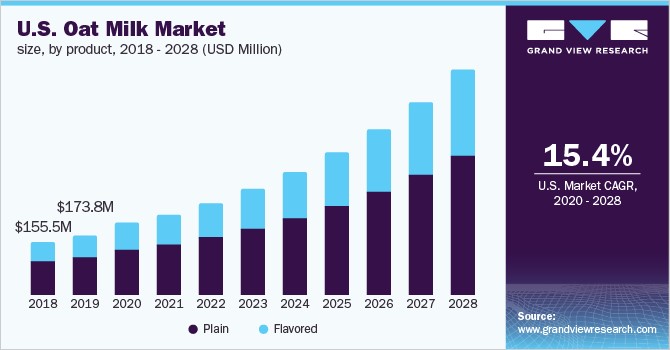
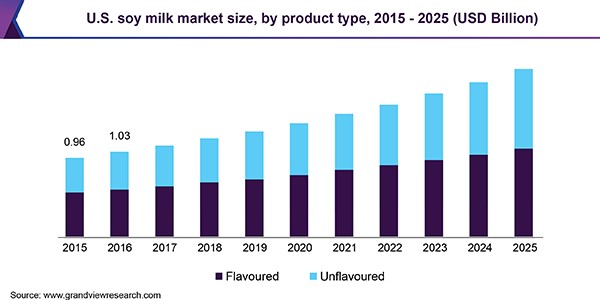
Evidence suggests that the rise in the rate of Autism correlates with an increase in the rate of vitamin D deficiency, associated with increased use of SPF sunscreens and high SPF cosmetics (see vitaminD), decreased Iodine intake in the population, decreased Selenium and Molybdenum in the soils, leading to functional vitamin B2 deficiency (See vitaminb2) and increased rates of veganism and vegetarianism in the population, contributing to the known association betwee vitamin B12 deficiency and developmental delay (see vitaminb12),and iron deficiency (see iron). This has been associated with a shift away from dairy milk - the major source of dietary vitamin B2, and a source of vitamin D - in fortified countries, and a source of Selenium. The shift has been to soy, almond and oat milk. Of these soy is goitrogenic (it contains the goitrogens genistein and daidzein), so too does oat milk, whilst almond milk contains cyanoglycosides (Chaouali et al, 2013), which will result in functional B2 deficiency which will result in paradoxical B12 deficiency, whilst the cyanoglycosides can inactivate vitamin B12.
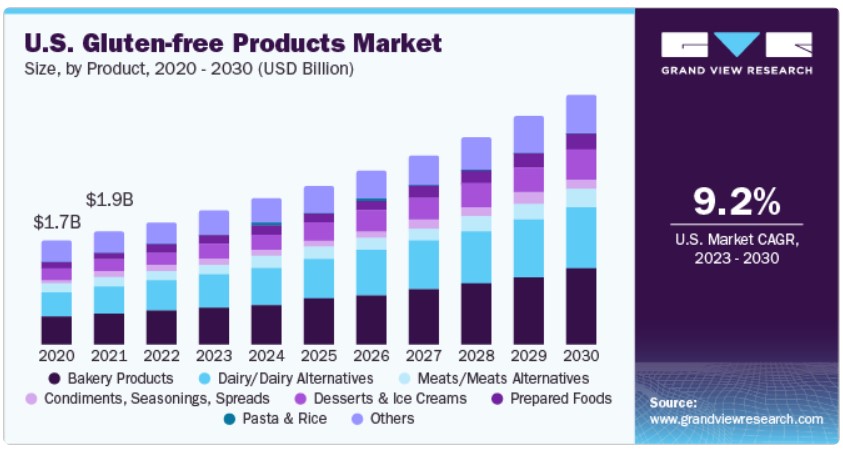
There has also been a dramatic rise in the rate of individuals who have adapted a gluten-free diet. This is despite the observation that the rate of ceoliac disease has not changed. Choosing to change from products that are fortified with folate, vitamin B1 and are naturally higher in iron, to products that are based on rice, and so exposed to higher levels of lead and arsenic. Hence, over the past 30 years there has been a major change in the nutrition of mothers, form those with a diet high in iron, B2, B12, folate, Iodine, Selenium and Molybdenum, so a diet that is deficient in iron, vitamin B12, vitamin B2, Iodine, Selenium, folate and vitamin B1. During this time the incidence of autism has changed form less than one in one thousand to now over one in thirty, in countries such as the US. Hence the diet of the average person has changed from being sufficient in iron, vitamin B12, Iodine, Selenium, Molybdenum, folate and vitamin B1, to, through the misguided choice of the population to one that is low in iron, vitamin B12, vitamin B2, vitamin B1, and folate and high in arsenic and lead. Little wonder that the incidence of developmental delay has increased from less than one in one thousand, to less than one in thirty. This increase has been solely due to the dietary choices of the mothers of these children!!.
Generally accepted beliefs on autism
Unfortunately, the general consensus on autism is Autism is a neurodevelopment and neurobiological disability that is not treatable or curable. It is not an illness or disease and most importantly, it is not inherently negative. Autistic people at Harvard and globally have advocated in the face of ableism to defend ourselves from such hateful, eugenicist logic. "
Research into the cause and treatment of the condition has more or less ground to a halt, with several large institutions publicly making policy statements to this effect. Further, some of these institutions have publicly stated that the only way to manage autism is through medication (See NPS). Hence the majority of organizations involved in Autism Spectrum Disorders using the condition as a gateway to funds that have been donated by those who wish to have progress in the treatment of the condition. This approach places a massive drain on the health budget of many countries, and in Australia, for instance, over one third of the National Disability Insurance funding goes to support people with autism. Further, it would appear that the major aim of most of the Autism Charities, is to propogate their services at considerable cost to those who use them, rather than to concentration on treatment and prevention of the condition. Further, these institutions openly declare that there is no cure for autism. However, the cause, treatment and prevention are relatively simple BUT, given the huge financial gain to those who run the various charities and those who treat the children, one is constantly reminded that: "While there is considerable financial gain to the medical profession for treating autism, there is little incentive for them to prevent or cure the condition"
In direct contrast to this position, our group has been actively involved in examining the metabolism of those with Autism Spectrum Disorder, with the main objective to find the cause(s) of the condition, and then potentially identify modes for treatment and prevention of the condition. It is therefore our aim to greatly improve the quality of life of not only those individuals who have the condition, but also those who have been involved in the care and maintenance of those with the condition. Further information is available at the sections on vitamin B2, vitamin B12, iron, vitamin D, and the NexusTheoryTM.
Previously it has been known that Vitamin B12 sufficiency is crucial for the development of myelination of the central nervous system, and poor vitamin B12 status is linked to poor growth and neurodevelopment. This condition was easily recognized by a simple blood test, which showed low serum B12, and was subsequently treated with vitamin B12 injections. "Modern day" Autism, is similar, however, individuals have functional B12 deficiency, which is brought about by functional B2 deficiency, and as such requires resolution of functional B2 deficiency before resolution of functional B12 deficiency can be achieved. In contrast to simple B12 deficiency, in functional B12 deficiency serum B12 may be normal or even very elevated, and hence other markers of activity are required for diagnosis. As such the children have paradoxical B12 deficiency. This can clearly be seen in the metabolic analysis of children with autism.
Autism - an example of extreme functional vitamin B12 deficiency
Autism: Vitamin B12 deficiency in disguise
Metabolic data obtained from over 2000 children from countries all over the world, has shown that the cause of autism is a functional vitamin B12 deficiency, as such the majority of signs and symptoms are identical to the developmental delay observed in children who are born quantitatively deficient in vitamin B12.
OCD and ADHD: Vitamin B12 deficiency in disguise
Data suggests that both OCD and ADHD are continuances of the spectrum of Vitamin B12 deficiency conditions, which include autism
Hence treatment for both conditions includes the use of SSRIs, and SNRIs, indicative of B12 deficiency, Just like autism, the rate of OCD has been increasing and is now at 2-3% of the US population. Up to 30% of OCD kids also have ADHD. Just like autism, the rate of ADHD has been rising with around 11% of kids having ADHD in the US (American CDC, 2022). As is the case for the majority of conditions associated with functional B12 deficiency, co-morbidities include anxiety (34%) depression (25%),, and sleep disorders, further strengthening the potential association with functional B12 deficiency. Metabolic analysis of children with ADHD showed evidence of functional B12 deficiency as measured by elevated homocysteine (Lukovac et al, 2024; Miniksar et al, 2022; Yektas et al, 2018; Saha et al, 2017; Namjoo et al, 2020) Similar associations with elevated homocysteine is seen in OCD (Balandeh et al, 2021; Yan et al, 2022; Türksoy et al, 2014; Esnafoğlu and Yaman, 2017; Atmaca et al, 2005; Wang et al, 2024), with low vitamin D also associated with increased rates of OCD (Esnafoğlu and Yaman, 2017) supporting the concept that OCD, ADHD, ASD are on the spectrum of functional B12 behavioural disorders.
Rights of children
According to the UNICEF charter on Children's rights, section 24. Health, water, food, environment " The Convention on the Rights of the Child: The childrens version | UNICEF
"Children have the right to the best health care possible, clean water to drink, healthy food and a clean and safe environment to live in. All adults and children should have information about how to stay safe and healthy."
Under the convention these rights extend to the unborn child.
In this regard, it has long been known that "Nutrition and consequently the development of the unborn baby is profoundly influenced by the maternal nutritional state from conception to birth." (Wahid and Fathy, 1987). Despite this, evidence is clear that every child that we have data for, who has developmental delay (ASD), DID NOT receive adequate nutrition whilst in the womb!
Tips on pregnancy, birth and raising children. There is a very useful site at https://raisingchildren.net.au/pregnancy
Diagnosis of Autism. Despite the fact that it has been known for over 40 years that deficiencies in any of Iodine, vitamin B12, or iron are associated with delayed mental development, early diagnosis of the condition does not assess these deficiencies, rather the child is generally assessed by a Psychologist. In addition the CRC now has a milestone AP CDCs Milestone Tracker App | CDC
Biochemistry of Autism. We have pooled our data on the Biochemistry of autism and how this is different from that in nutritionally normal individuals and have described this in sections devoted to Iron Deficiency, Vitamin B12 deficiency, Vitamin B2 deficiency and vitamin D deficiency. In addition there is a section on glucose metabolism in autism.
Nexus TheoryTM of Development of Autism. Examination of pooled data that we have collected on the Biochemistry of Autism and the Genetics of Autism, a central, or meeting point of convergence, or a Nexus has become apparent. This is the basis of the "Nexus Theory" of Autism, which is discussed on the site.
Myths surrounding the cause and treatment of Autism. Due to the lack of understanding of the biochemistry of autism, there are many myths surrounding the cause and treatment of autism. https://understandingautism.com.au/myths.htm
Prevention of Autism. Through the analysis of the factors conditions that contribute to the development of ASD, we believe that it may be possible to detect the condition much earlier than currently occurs, and also we believe that it may be possible to prevent the condition and have dedicated a section to prevention All of data supports the notion that nutritional deficiency in the womb is the major cause of autism in the child.Treatment of Autism. Through the analysis of the factors conditions that contribute to the development of ASD, we have developed a treatment regime to enable children overcome the deficiencies that are implicated in the developmental delay in ASD, and so optimize the chance of normal development in these children.
Development of Receptive language. Often children with ASD have poor receptive language. They may have difficulty paying attention to conversation, poor eye/face contact, and have poor literacy, and expressive language. see Receptive Language (understanding words and language) - Kid Sense Child Development and Receptive language development in children aged 0-5 years | Child Development Institute
Additional Information on Autism. There are many "help" sites that can give you information on behaviour, learning difficulties, social interaction, difficulties that people with autism experience etc. One that looks to be particularly helpful is https://www.autismhelp.info/. If you know of others please let us know.
Autism Assessment Tool. A new tool has been developed by the group at Early Autism Detection which claims to be able to detect the potential for a child to develop autism with an 81% accuracy. The tool is easy to you and comes as a series of down-loadable Apps. There is also a behavioural assessment tool developed by Brazelton
Special Thanks. We would particularly like to thank all of the mums and dads who have generously provided the data that has enabled us to explore the biochemistry and genetics of the condition and we hope that through the information provided on this site that they may better understand the condition, why it has developed and what they can do about it.
Helpful Contacts. Whilst we can help you to understand what we know about the development and treatment of the condition, there are many wonderful sites offering emotional and practical support on being a "special needs parent". We have included some of these sites on our Contact page. Please tell us if you have used particularly useful sites and we will endeavour to add them to the page.
Biochemistry of Autism. Data presented in subsequent pages has been obtained by the Understanding Autism Research Group (UARG), through the analysis of metabolic data supplied by over 600 parents with children with ASD..
Research. Data on B12 deficiency and autism
References. For those whom are interested, we have included relevant references to validate our conclusions.
Vitamin B12 deficiency and sleep disorders
Functional Vitamin B2 Deficiency in Autism (fortunejournals.com)
Altered Neurotransmitter Metabolites in vitamin B12 deficiency
Jiet al. (2020). Association of Cord Plasma Biomarkers of In Utero Acetaminophen Exposure With Risk of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Childhood. JAMA psychiatry, 77(2), 180189. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3259etal.
Folstein etal Genetics of autism: complex aetiology for a heterogeneous disorder. Nature Reveiws Genetics 2001; 2, 9430955
Mazumdar etal, The spatial structure of autism in California 1993-2001 https://www.ncbi.nlm.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2835822/
https://www.brazelton.co.uk/courses/neonatal-behavioural-assessment-scale-nbas/
Wahid, M.A., Fathi, S.A.H. Nutrition and the unborn baby. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 17, 199 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912532
Autism rates in Australia growing faster than global average (smh.com.au)
Chaouali N, Gana I, Dorra A, Khelifi F, Nouioui A, Masri W, Belwaer I, Ghorbel H, Hedhili A. Potential Toxic Levels of Cyanide in Almonds (Prunus amygdalus), Apricot Kernels (Prunus armeniaca), and Almond Syrup. ISRN Toxicol. 2013 Sep 19;2013:610648. doi: 10.1155/2013/610648. PMID: 24171123; PMCID: PMC3793392.
Lukovac T, Hil OA, Popović M, Jovanović V, Savić T, Pavlović AM, Pavlović D. Serum Biomarker Analysis in Pediatric ADHD: Implications of Homocysteine, Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, Ferritin, and Iron Levels. Children (Basel). 2024 Apr 22;11(4):497. doi: 10.3390/children11040497. PMID: 38671715; PMCID: PMC11048887.
Miniksar DY, Cansız MA, Kılıç M, Göçmen AY. Relationship between sleep problems and chronotypes of children and adolescents with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder and serum GABA, glutamate and homocysteine levels. Chronobiol Int. 2022 Mar;39(3):386-397. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2021.2018452. Epub 2021 Dec 27. PMID: 34961406.
Yektaş Ç, Alpay M, Tufan AE. Comparison of serum B12, folate and homocysteine concentrations in children with autism spectrum disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and healthy controls. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019 Aug 6;15:2213-2219. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S212361. PMID: 31496704; PMCID: PMC6689552.
Saha T, Chatterjee M, Sinha S, Rajamma U, Mukhopadhyay K. Components of the folate metabolic pathway and ADHD core traits: an exploration in eastern Indian probands. J Hum Genet. 2017 Jul;62(7):687-695. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2017.23. Epub 2017 Mar 2. PMID: 28250422.
Namjoo I, Alavi Naeini A, Najafi M, Aghaye Ghazvini MR, Hasanzadeh A. The Relationship Between Antioxidants and Inflammation in Children With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2020 May-Jun;11(3):313-321. doi: 10.32598/bcn.11.2.1489.1. Epub 2020 May 1. PMID: 32963724; PMCID: PMC7502190.
Balandeh E, Karimian M, Behjati M, Mohammadi AH. Serum Vitamins and Homocysteine Levels in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychobiology. 2021;80(6):502-515. doi: 10.1159/000514075. Epub 2021 Mar 19. PMID: 33744893.
Yan S, Liu H, Yu Y, Han N, Du W. Changes of Serum Homocysteine and Vitamin B12, but Not Folate Are Correlated With Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Front Psychiatry. 2022 May 9;13:754165. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.754165. PMID: 35615448; PMCID: PMC9124900.
Türksoy N, Bilici R, Yalçıner A, Ozdemir YÖ, Ornek I, Tufan AE, Kara A. Vitamin B12, folate, and homocysteine levels in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Sep 9;10:1671-5. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S67668. PMID: 25228807; PMCID: PMC4164291.
Esnafoğlu E, Yaman E. Vitamin B12, folic acid, homocysteine and vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2017 Aug;254:232-237. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.04.032. Epub 2017 Apr 21. PMID: 28477545.
Atmaca M, Tezcan E, Kuloglu M, Kirtas O, Ustundag B. Serum folate and homocysteine levels in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005 Oct;59(5):616-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2005.01425.x. PMID: 16194269.
Wang S, Zhang X, Ding Y, Wang Y, Wu C, Lu S, Fang J. From OCD Symptoms to Sleep Disorders: The Crucial Role of Vitamin B12. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2024 Nov 19;20:2193-2201. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S489021. PMID: 39583014; PMCID: PMC11585301.
Copyright © 2014 B12 Oils. All Rights Reserved.
Reproduction in whole or in part in any form or medium without express written
permission is prohibited